CB786-UNIVERSITY OF KENT-Operation Management-PROBLEMS AND SOLUTIONS
| CODE | UNIVERSITY | WORDS COUNT | REFERENCE |
| CB786 | UNIVERSITY OF KENT | 2000 | APA |
QUESTIONS:
1) A time-study was conducted to determine the standard time in a sandwich- making operation. They found that workers take on average 2.5 minutes to make a batch of 5 sandwiches as demonstrated in the table below:

a) Given a performance rating of 70% calculate the basic time in minutes.
b) If a fixed allowance of 1 hour for lunch break is given every day, what is the standard time for one sandwich in minutes? Assume worker works 8 hours in a day including lunch break (7 hours work, 1 hour idle).
c) A new operations manager wants to cut the lunch break from 1 hour to 20 minutes claiming that he would increase the daily sandwich production by almost 10%. Do you agree with his claim? Explain it though calculations.
2) At home, I have 12 bottles of whisky in my bar. On average, I finish and
purchase one new whisky bottle every two months.
a) What is the average time each whisky bottle stays in my bar?
b) Little’s Law considers the average number of items in a queuing system based on the average time to process a single item. However in reality what is the longest and shortest time an individual bottle of whisky may stay in my bar? Explain your answer and any assumptions you made.
3) A company has a starting balance of 15 items (Week 0) and receives
10 items each week (starting in week 1) with a lead-time of 2 weeks. Based on the following customer demand for its products:
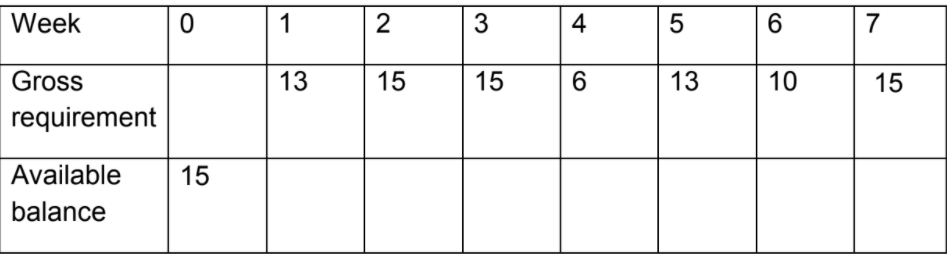
a) Determine which week the company will stock out (show your
calculations). What does this mean for their customer?
b) If you need to avoid stock outs at any cost, what would you do? In
practice, what would be the implications of your recommendation?
4) A computer factory in Japan produces three different types of servers: 400 TB, 200 TB and 100 TB. The 400 TB drive can be assembled in 3 hours, the 200 TB in 2 hours, and the 100 TB in 0.8 hours. There are 530 staff hours of assembly time available each week. If demand for the 400, 200 and 100 TB servers is in a ratio of 3:4:5 (12 units), answer the following questions:
a) What is the time needed to assemble the set of 12 units?
b) How many units are produced per week (rounded to the nearest whole number)?
5) This case concerns the issues of re-developing operations strategy and re-
designing services and products to meet the evolving needs of customers.
a) Compared with a conventional high-street furniture store, what is the relative importance of the operational performance objectives in the traditional IKEA ‘big box’ stores? Consider drawing a polar diagram to illustrate your points
b) What trade-offs do IKEA customers make when they go to IKEA big
stores (instead of conventional high-street furniture stores)? How does
IKEA new operational approaches (web-based retailing, small store,
task-based service finder, etc.) impact these trade-offs?
Answer ( 1 )
Ikea is such a brand that tends to look at the future. As per the case study it is stated that the strategy of Ikea in terms of providing the furnishings at the low prices that tends to present value for money with a huge range with regards to the choice. On the other hand, it can be said that the performance objectives highlights the reason that the customers purchase services or goods from a company in the preference of their potential competitors. It has been defined by some of the scholars that there are 5 differences of the performance objectives and these are mainly the speed, quality, cost, flexibility as well as the dependability.