INTRODUCTION TO 2G NETWORK
2G Network is being regarded as the short generation for mobile technology. In other words, it can be said that the 2G network is basically a type of cellular network that was commercially being launched on the GSM standard in Finland by Radiolinja in the year 1991.
On the other hand, it can also be depicted that 2G network is being regarded as second generation wireless telephony technology that tends to replace analog 1G technology. This indicates that there is enormous development had happened in cellular technology.
Additionally, the second-generation mobile technology has completely changed the concept of mobile phones. The respective technology has enabled users to gain the advantages in the form of the increased frequency band, high data transfer rate, and the wireless connectivity, etc.
However, at present, the technology of mobile communication has evolved to 5G technology. But, in the given blog we will gain a thorough understanding of the 2G network technology. In this regard, we will basically see the working process behind the respective technology. Further, this blog will also entail about the benefits as well as the limitations that are associated with the 2G network in an effectual way. Online Assignment Help will provide you with more details on assignment related to Networking.
FACTS AND FEATURES RELATED TO 2G NETWORK
There are some facts and features of 2G network examined. These features will assist an individual in the task of assessing the 2G technology among different other forms of network technologies. The description in relation to the same is given below:
- For the processing purpose, digital signals are used instead of analog signals that are being employed in a 1G network.
- The digital signal processing that is being used in the 2G network will allow the network to give support to the voice traffic and the data transfer.
- It connects mobile devices with the internet and the different other types of business networks.
- It has the speed of around 135 kbps (Kilobits per second) which is equivalent to the 1000 bits per second.
- In the year 2001, the 2G network is being phased out by 3G networks. For guidance related to computer science and programming you can check programming homework help
TYPES OF TECHNOLOGIES USED IN 2G NETWORK
Before improving the knowledge about the working process that is being associated with the 2G network, it is very much beneficial for the individual that it should have a proper understanding about the technologies that are used in 2G.
This is due to the fact that lack of knowledge of the same will not enable individual to improve better understanding of the given network. The details about all the technology are given below:
• FDMA (Frequency Division Multiple Access): FDMA is being defined as the channel access method that is being used in some of the multiple access protocols. The respective technology gives the opportunity to the multiple users with respect to send the data by using a single channel of communication such as microwave beam or the coaxial cable etc.
Further, it tends to divide the bandwidth of the channel into the separate non-overlapping frequency of the sub-channels. In addition to this, here each sub-channels are allocated separately to the different users. The given form of technology is basically used in the satellite communication system as well as in the telephone trunklines.
On the other hand, the FDMA enables the call with regard to use varied frequency and for this purpose, it splits calls into different small cells. Further, it is also examined that FDMA works best in the analog transmission but it does not mean that it will not provide support to the digital transmission. Although it is giving services of digital transmission, the services which are being given by it is very much poor.
• TDMA (Time Division Multiple Access): It is also being regarded as another form of mobile phone technology that is being used in 2G network. It is being regarded as the channel access method that is being used in the shared medium method. The respective technology gives the opportunity to the user with respect to sharing the channel of the same frequency by dividing the signals into the different types of time slots in an effectual way.
In addition to this, it also allows the multiple stations to use the same medium of transmission while using only some part of the channel capacity. In addition to this, the given technology was first used in the satellite communication system by the Western Union. However, at present, it is extensively used in the passive optical network and combat net radio system. Thus, it can be said that it is a more advanced form of mobile communication technology and it is related to the 2G network.
Further, it uses different types of technologies such as GSM (Global System for Mobile Communication), IDEN (Integrated Digital Enhanced Network) and PDC (Personal Digital Cellular). Herein, on the basis of the analysis, it is also examined that TDMA is 30 KHz wide and around 6.7 milliseconds long. It is being divided into three major slots of time.
It uses compression and decompression algorithm with an aim to compress the digital information. The division of this narrow band into three-time slots tends to raise the overall capacity of the frequency band. It also gives support to the frequency bands such as IS-54 and IS-136.
• CDMA (Code Division Multiple Access): The third and final form of 2G network mobile technology is CDMA. This technology is being used by different types of radio communication technologies. In other words, it can also be said that it is being regarded as a very good example of the multiple access in which several transmitters can send information simultaneously over the single channel of communication in an effectual way.
Further, it also gives the opportunity to the user with respect to sending the band of frequencies. Additionally, the given method tends to employ a special type of coding scheme and spectrum technology. In other words, it can be said that the respective technology is contrary to the TDMA. This is due to the reason that CDMA works in a singular way. Its main activity is to convert the information into digital data.
The incoming calls which received here are spread on the surface of the channel. It also compresses the data into different small packets and thus these packets are being sent to the separate frequency columns. It gives support to the interim standard of around 95 and it also gives support to the operation at the frequency band of around 800 MHz to 1900 MHz.

HOW 2G NETWORK WORKS?
Till now we have improved our understanding of the major technologies that are related to 2G network. However, in the respective section, we will look into the detail process behind the 2G network. It can be said that the 2G network is also called by the name of GSM. 2G network architecture is being used with an aim to explain the working process behind the given technology.
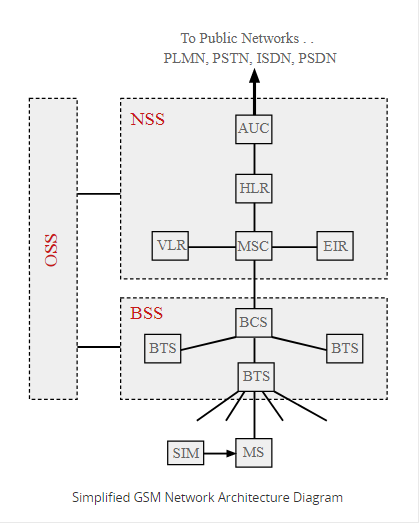
There are four main areas are related to the 2G network. These are Network and Switching subsystem, Base Station Subsystem, Mobile station, and Operation, and support subsystem.
NETWORK AND SWITCHING SUBSYSTEM (NSS)
It is being called by the name of a core network of GSM. It provides main control to the 2G network and thus it interfaces the whole mobile network. It contains different major elements and description of the same is given below:
- Mobile Services Switching Center (MSC): It is the main element of the GSM core network area. It plays the role of normal switching node within PSTN or ISDN. It offers additional functionality with the help of which the need of mobile users can be supported. This comprises of registration, call location, authentication, routing of calls to the mobile subscribers and inter-MSC handovers. It holds very limited information about BTS and BSC that are attached to it. This has its own backups as well as configuration. Its main function is to translate the number dialed and route the same to the correct GMCS. It also controls some part of the call set up. It contacts the HLR and controls the handovers when different other MAC is involved in the same. MSC passes alarms as well as performance data to the monitoring system. In addition to this, it also generates the charging data and passes the same to the CG.
- Visitor Location Register (VRL): This possesses selected information from the HLR and thus provides selected services for the individual subscribers. It is being considered as an integral part of MSC, but it can be implemented as a separate entity. It is through such type of activity only access can become more faster as well as convenient.
- Equipment Identity Register (EIR): It basically holds the black, grey and white list of mobile phones. Thus, it makes the decision that whether specific mobile should be given permission to operate on network or not. Here, each mobile has a specific number and it is called by the name of International Mobile Equipment Identity. The number is installed in the EIR and it is checked by the network at the time of registration.
- Home Location Register (HLR): It plays the role of the database for all kind of administrative information about the subscriber. It basically possesses the data about subscriber last location. Here, it routes the calls to the base station of relevant MS. Here, when the user switches on the phone then in this situation the phone registers itself with the network. Here, it is through this way only information about the BTS is examined. Hence, on the basis of the given information, only an incoming call is routed to the appropriate location. Further, it periodically re-registers the phone when it is not in an active position. Through this way HLR aware about the latest position of mobile phone.
- Authentication center (AUC): It is being regarded as the protected database which contains the secret key in the SIM card of the user. It is basically used for the authentication and ciphering on the radio channels. Thus, these are being considered as the main element of NSS. Check Assignment Help Australia for more detailed information on any subjects.
BASE STATION SUBSYSTEM (BSS)
This system main function is to communicate with the mobile phone over the network. It has two major elements and these are given below:
- Base Transceiver Station (BTS): It is used in the GSM network and it possesses the radio transmitter-receivers and associated antenna that tends to communicate directly with the mobile phones. It receives the radio waves and converts the same into the digital format with an aim to transmit the same to the BSC. In addition to this, BTS takes the digital signals from BSC and convert the same into the radio waves and transfer the same to the mobile station in an effectual way. Apart from this, it also monitors the quality as well as the level of radio signals and reports about the same to BSC. Here, BSC takes the decision that whether MS need to receive from another BTS or not. Further, it also has a feature that it holds the software as well as configuration for itself. Thus, it plays the role of a bridge between BSC and MS.
- Base Station Controller (BSC): It is another element of BSS. Its main function is to send as well as receive calls for entire BTS on the network. It monitors the quality as well as levels of MS and BTS reports along with this it also controls the MS that is associated with its area. It communicates with all the BTS and it is termed as the Abis Interface.

MOBILE STATION
It is the mobile equipment and it is basically known from the name of a mobile phone and cell phone etc. From last many years the size of mobile phones has fallen drastically, but there is a significant increment is being examined in the overall functionality of the mobile phone. There are two main elements of cell phone and these are SIM and main hardware. The hardware of the mobile phone includes battery, case, display, and data receiver, etc. On the other hand, mobile station possesses a number and it is called by the name of (IMEI) International Mobile Equipment Identity.
This number is installed on the phone by the manufacturing company and it cannot be changed. At the time of registration, it is being accessed by the network with an aim to check whether the mobile is being reported as stolen or not. In addition to this, SIM is the type of identity card for the user of the phone. This card identifies the user over the network. Thus, it can be said that with the help of a mobile station, suitable information about the user can be gained.
OPERATION AND SUPPORT SUBSYSTEM
It is also being called by the name of OSS. This system is connected to NSS and BSC. The main function of operation and support subsystem is to monitor as well as control the overall GSM network. Additionally, the system is also used with an aim to put control over the BSC traffic load. It can be said that BS is related to the subscriber number.
Here, as the number of BS increases then in this situation, the task to perform the maintenance function gets transferred to the BTS. This will help in saving the cost of ownership of the system. The 2G GSM network complies with the logical method of operation. It is very much easy method than the current mobile phone. However, it is to be evaluated that the 2G network architecture does not showcase operational and voice basic functions that are essential in the mobile phone.
ADVANTAGES OF 2G NETWORK
Till now we have discussed many internal things about the 2G network, now it’s time to gain further details about the same. As a result of this discussion is being carried out on the advantages that are related to the 2G network.
- Improved privacy: It is being regarded as another most effective advantage that is related to the 2G network. Herein, it can be said that in comparison to 1G, the 2G network tends to offer improved privacy. In this regard, it can be said that privacy is being regarded as the biggest matter of concern for many users. Thus, if this will be ignored then in this situation user may quickly move on to the better and effective services in an effectual manner.
- Lower power emission: The 2G technology does not consume much power like the 1G. Thus, it has helped in the task to deal with different health concerns that are associated with the mobile technology.
- It has introduced many services: After the evolution of 2G network there are many digital services has evolved. It comprises of email and SMS etc.
mobile phone.
LIMITATION OF 2G NETWORK
- Signal problem will be there if network coverage is not there in a specific area.
- It cannot handle the complex data like video.
